AddressBokeljska 7, Belgrade
Contact phone+381 11 3910 112, +381 11 3910 115
Working hoursMonday - Friday, 10AM to 6PM

Sinonimi: Benign histiocytoma, fibrous histiocytoma
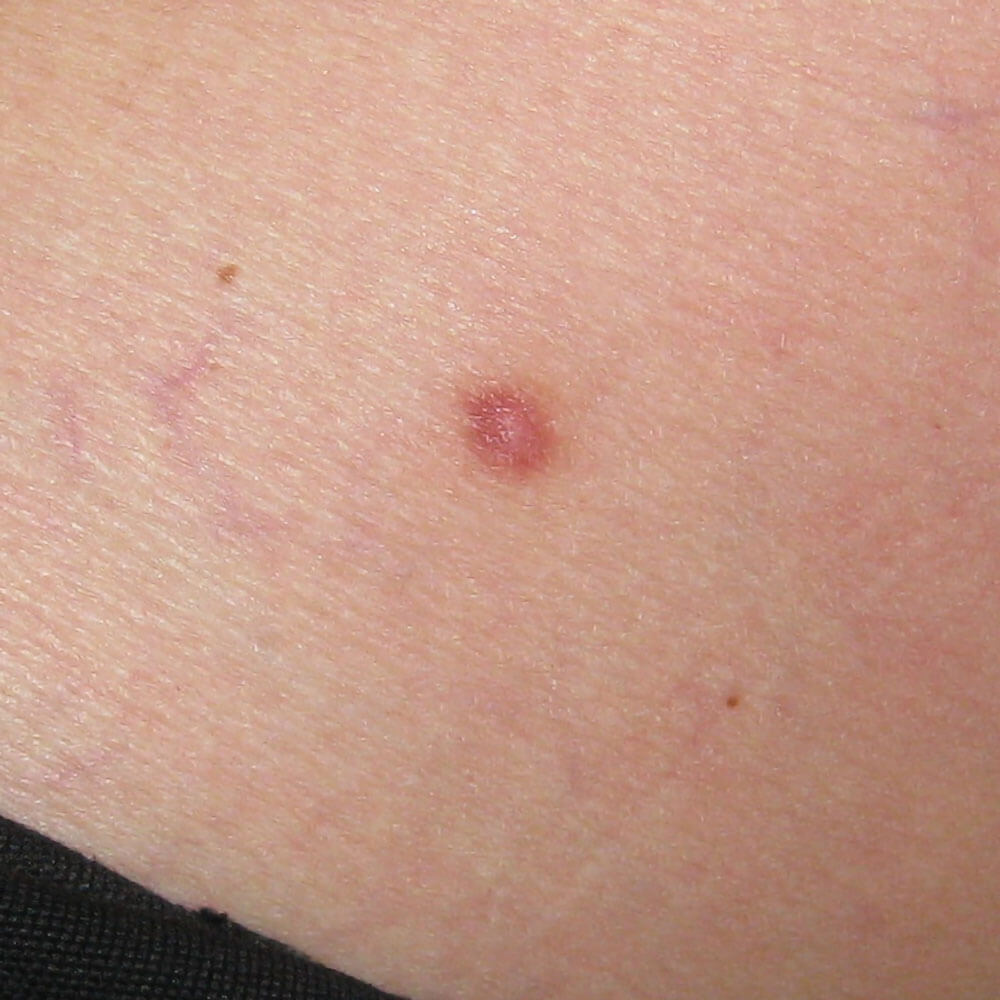
Dermatofibrom na nozi

Dermoskopski nalaz
The real reason for formation of these skin lesions is unknown. Microtrauma of the skin can be cited as one of the possible causes.
They are usually brownish lumps in the skin, sizing from a few mm to a centimeter with a whitish center. In most cases they are painless, and in a small number of cases patients cite pain or itching in the region.The size can rarely get larger, but the intensity of the color may change over periods of time.
Diagnosis is easily made by clinical examination ( by eye), and dermoscopy. Biopsy is rarely needed.
If it doesn’t cause any nuisance and doesn’t present an esthetical issue, it can be left untreated.
Still, if it grows, it’s important to preventively remove it, and the method of choice is an excision.
Repeated microtrauma to the skin is considered a risk factor (punctures, depilation, mosquito bytes…)
Risk group is considered to be women after the age of 40, because of the decrease in estrogen hormones.
No, it’s not always necessary to remove dermatofibromas because they are benign skin lesions.
But, if it grows or changes, removing it for preventive reasons is advised.
No, but a new one can form near the site of the old one or on other regions.
Usually it appears in women, on the legs.
Synonyms: Benign histiocytoma, fibrosus histiocytoma

Dermatofibrom na nozi

Dermoskopski nalaz
Dermatofibrosarcoma protuberans, Melanocytic lesions (Nevus), Dysplastic Nevus, Spitz Nevus, Blue Nevus, Keloid, Keratoacanthoma, Melanoma, Basal Cell Carcinoma, Squamous Cell Carcinoma.
Reasons for formation of dermatofibroma are still unknown. The place of skin microtrauma (from hair removal to insect bites) is still not known well enough.
Presentation of dermatofibromas on the skin is commonly without any symptoms.
Complications of dermatofibroma are very rare. Specail attention should be devoted to cases that present an evolution of the lesion, i.e. if it grows, changes color or loses it’s typical appearance. Digital dermoscopy and biopsy diagnostics are advised in all of those cases.
Risk factors for developing dermatofibromas, at least incidence-wise are:
Real prevention doesn’t exist, but based on the risk factors, kepping Your skin away from microtrauma, especially for women when waxing, can reduce the risk of developing dermatofibroma.